An Introduction to laser source
Table of Contents
1. Semiconductor Laser Light Source Series (Tunable Laser)
2. What is a Laser Light Source?
3. What is a Laser Light Source?
3-1. Characteristics of Laser Beams
3-2. Mechanism of Laser Light Sources
4. Types and Applications of Laser Light Sources
4-1. Characteristics of Various Laser Light Sources
4-2. Laser Light Source Application Examples by Industry
5. Advantages of Koshinko Optical Industry’s Laser Light Sources
5-1. Narrow Laser Linewidth
5-2. Low Noise
6. Summary
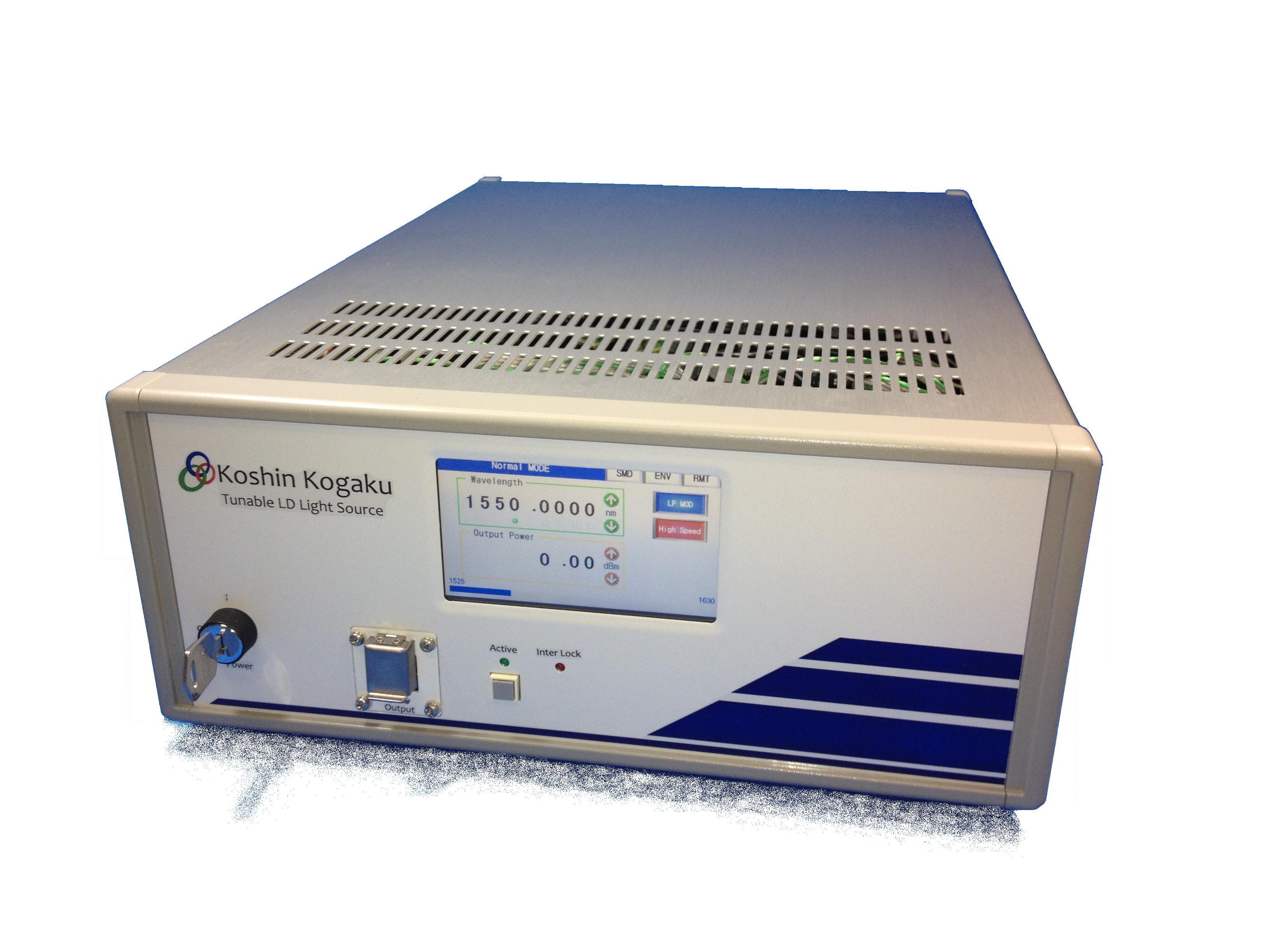

1. Semiconductor Laser Light Source Series (Tunable Laser)
High-resolution type Wavelength Tunable Diode Laser
KLS-601A Series
Standard type Wavelength Tunable Diode Laser
KLS-201A Series
Fixed-Wavelength Semiconductor Laser
FLS, FLM
2. What is a Laser Light Source?
Are you familiar with the characteristics and applications of laser light sources? This article clearly explains the types, features, and practical examples of laser light sources. Gain knowledge that will benefit your research and product selection, empowering you to confidently tackle laser technology!
3. What is a Laser Light Source?
The term “laser” is an acronym for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.” In other words, a laser light source is a light source that amplifies and emits light using the special physical phenomenon of stimulated emission.
3-1. Characteristics of Laser Beams
Laser beams play an extremely important role in our lives and in science and technology due to their unique characteristics and the complex mechanisms that generate them.
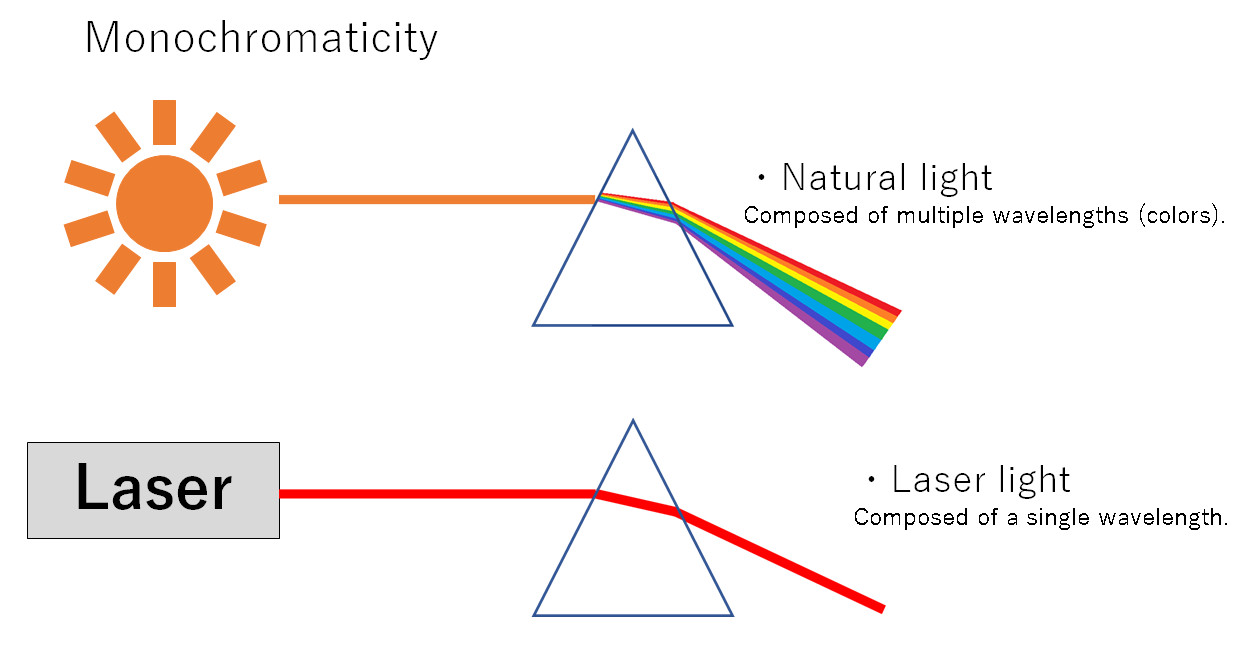
・Monochromaticity
They consist of light of nearly a single wavelength (color). For example, the light from a red laser pointer is pure red, containing almost no other colors.
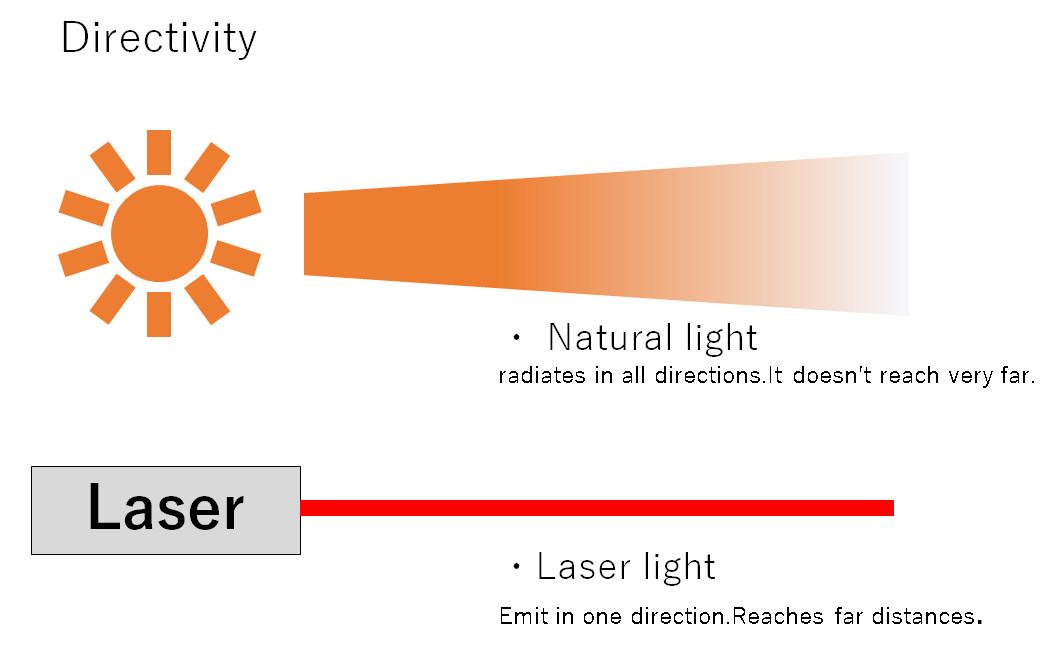
・Directivity
Travels straight and far with minimal spread. Unlike a flashlight beam that widens with distance, a laser beam maintains an extremely narrow beam.
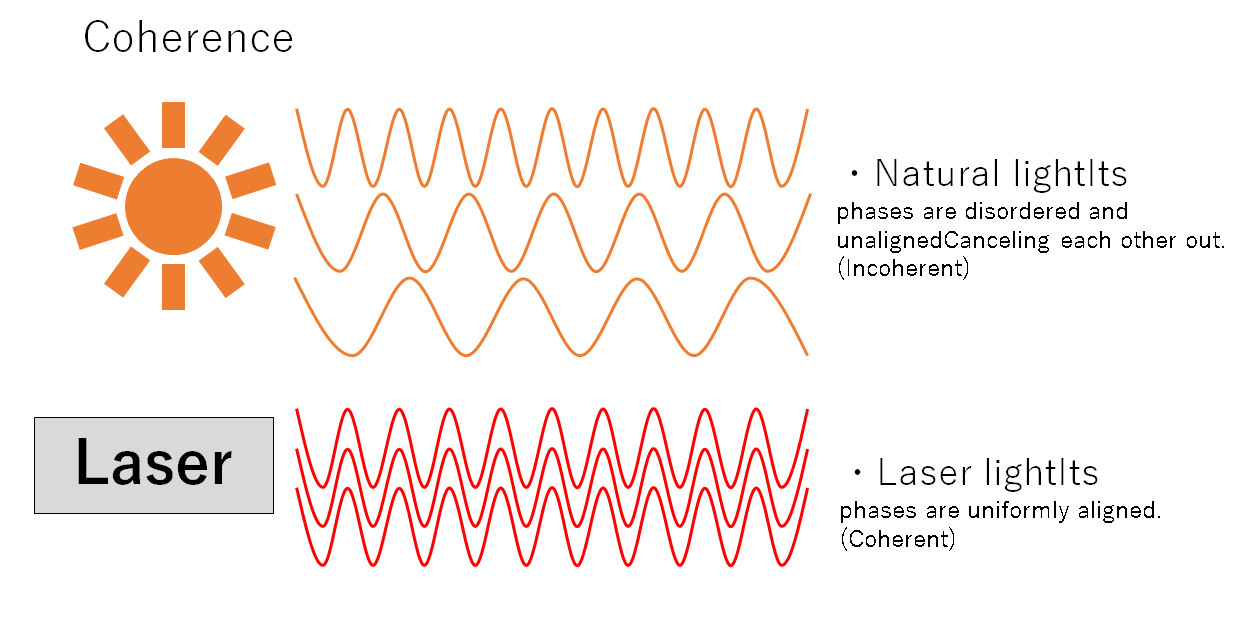
・Coherence
The timing (phase) of the peaks and troughs of light waves is neatly aligned both temporally and spatially.
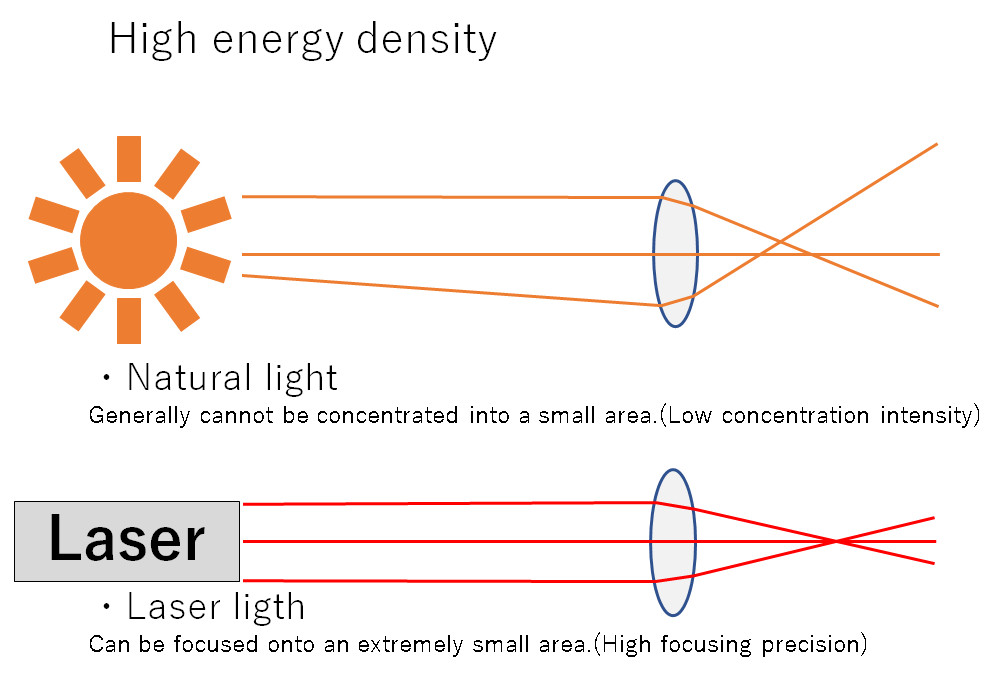
・High energy density
Capable of concentrating an extremely large amount of energy within a small area.
3-2. Mechanism of Laser Light Sources
Laser light sources are technologies that generate powerful beams by amplifying light. The fundamental mechanism involves exciting an active medium and repeatedly reflecting light within a resonator to amplify light of a specific wavelength. This results in laser light being highly directional and possessing a much higher energy density compared to conventional light sources. These characteristics enable laser light sources to be applied in a wide range of fields, including high-precision processing, measurement, and communications. Furthermore, laser light sources have driven innovation across numerous fields, with their applications expanding daily.
4. Types and Applications of Laser Light Sources
Laser light sources possess distinct characteristics based on their oscillation medium and are utilized across diverse fields.
These laser light sources contribute to innovative technologies and product development that leverage their unique properties in a wide range of fields, including medicine, industry, entertainment, and education, enriching our lives.
4-1. Characteristics of Various Laser Light Sources
Laser light sources come in various types, including solid-state lasers, semiconductor lasers, gas lasers, and fiber lasers. Solid-state lasers are characterized by high output power, while semiconductor lasers are easily miniaturized. Gas lasers provide stable wavelengths, and fiber lasers offer high efficiency. It is crucial to select the optimal laser light source by leveraging these characteristics according to the application. Specifically, in the medical field, they are used for tissue incision and treatment; in industry, for precision machining and material analysis; and in entertainment, for creating visual effects. Furthermore, these laser light sources demonstrate their effectiveness in education. For example, students using lasers in science experiments enhances learning quality and helps bridge theory and practice. Leveraging laser characteristics, their application continues to expand across diverse fields.
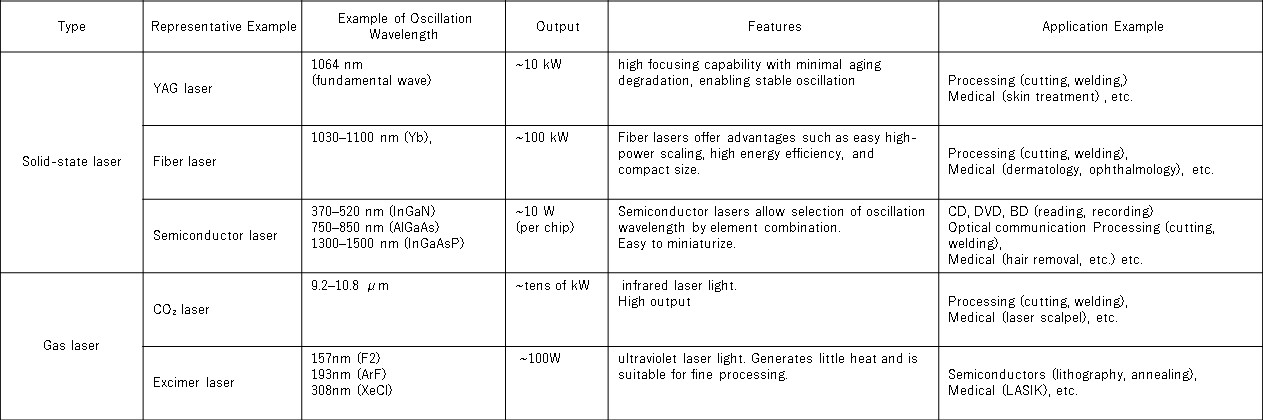
4-2. Laser Light Source Application Examples by Industry
Laser light sources are utilized in manufacturing for cutting and welding, in the medical field for surgery and treatment, and in communications for data transmission. They are also employed in the entertainment industry for shows and display technologies. The adoption of laser light sources across these industries maximizes their unique properties, contributing to improved efficiency and precision. Furthermore, the high energy density of laser light sources is driving significant innovation in new material development and space exploration technology, making them indispensable for future technological advancements. Moreover, laser light sources are beginning to be utilized in food processing and agriculture, opening new avenues for quality improvement and efficient production. This contributes to future food supply as a sustainable production technology. The evolution of laser technology continues to offer new possibilities across all industries.
With the advancement of laser light source technology, laser light sources have become smaller and more portable. This enables their use in various field settings, meeting a wide range of needs. The latest technologies utilizing laser light sources are advancing the precision of medical equipment and enabling efficient production processes in industrial machinery, making them indispensable for future technological innovation.
5. Advantages of Koshinko Optical Industry’s Laser Light Sources
The most noteworthy features of our laser light sources are their narrow laser linewidth and low noise.
5-1. Narrow Laser Linewidth
Our laser light sources boast an extremely narrow laser linewidth. A narrow linewidth enables higher precision measurements, delivering more accurate and reproducible results for applications in scientific experiments and medical fields.
5-2. Low Noise
our laser light sources are characterized by low noise, making them highly reliable. This low noise level ensures the accuracy of results, a crucial factor for researchers and engineers. Low-noise laser light sources are expected to find applications in many fields going forward, with demand anticipated to increase.
6. Summary
Laser light sources possess characteristics such as monochromaticity, directionality, interferability, and high energy density, making them indispensable across diverse fields including medical, industrial, communications, and entertainment applications. Their high performance is particularly sought after in precision processing, analysis, and surgical and therapeutic procedures in medical settings.
Our laser light sources, characterized by “narrow laser linewidth” and “low noise,” are ideal for research, medical, and industrial applications where measurement accuracy and reproducibility are paramount. We also offer customization to meet specific customer requirements and provide recommendations for the optimal light source. If you are considering selecting or introducing a laser light source, please visit our service page.
Please feel free to inquire us
